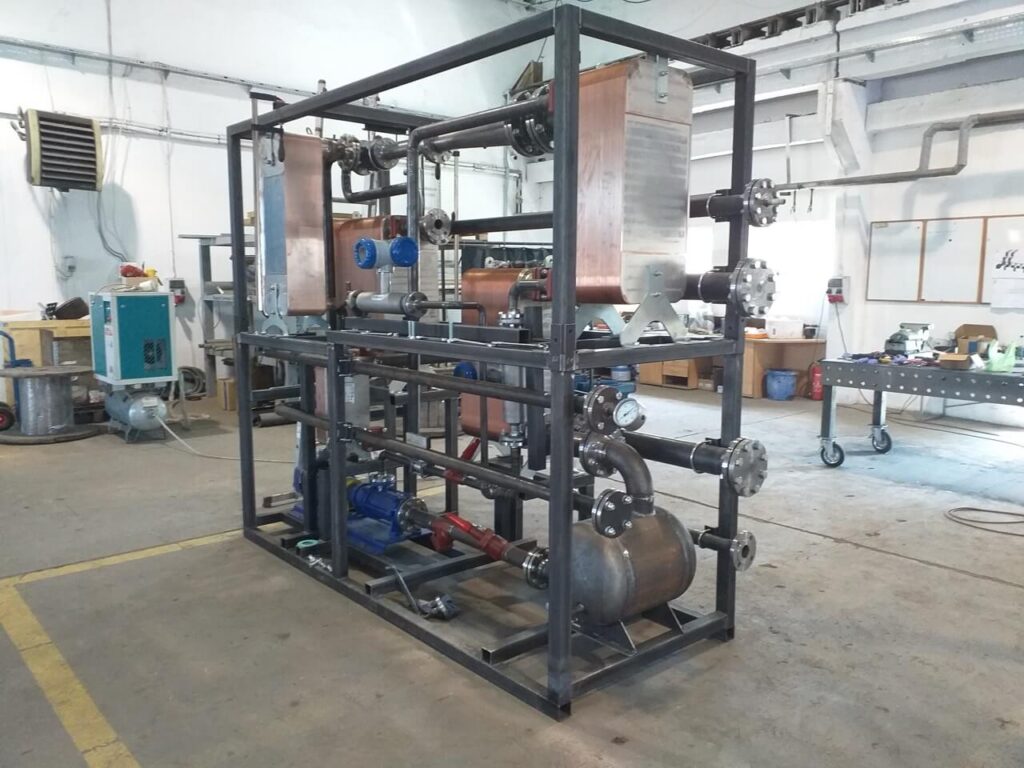
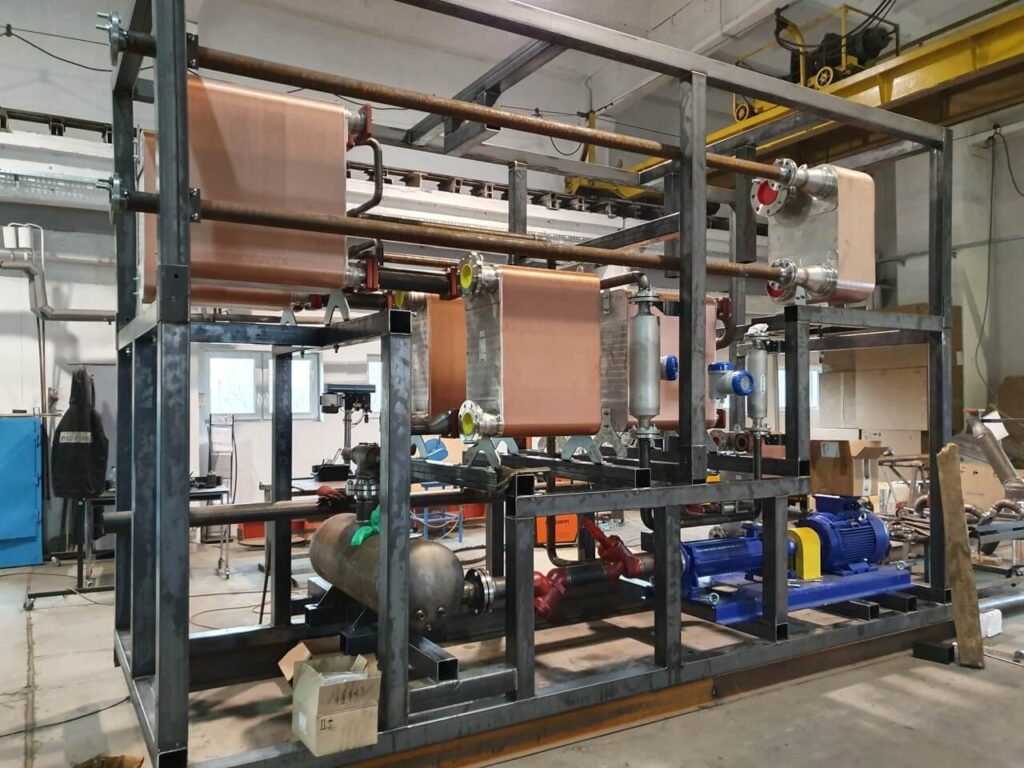
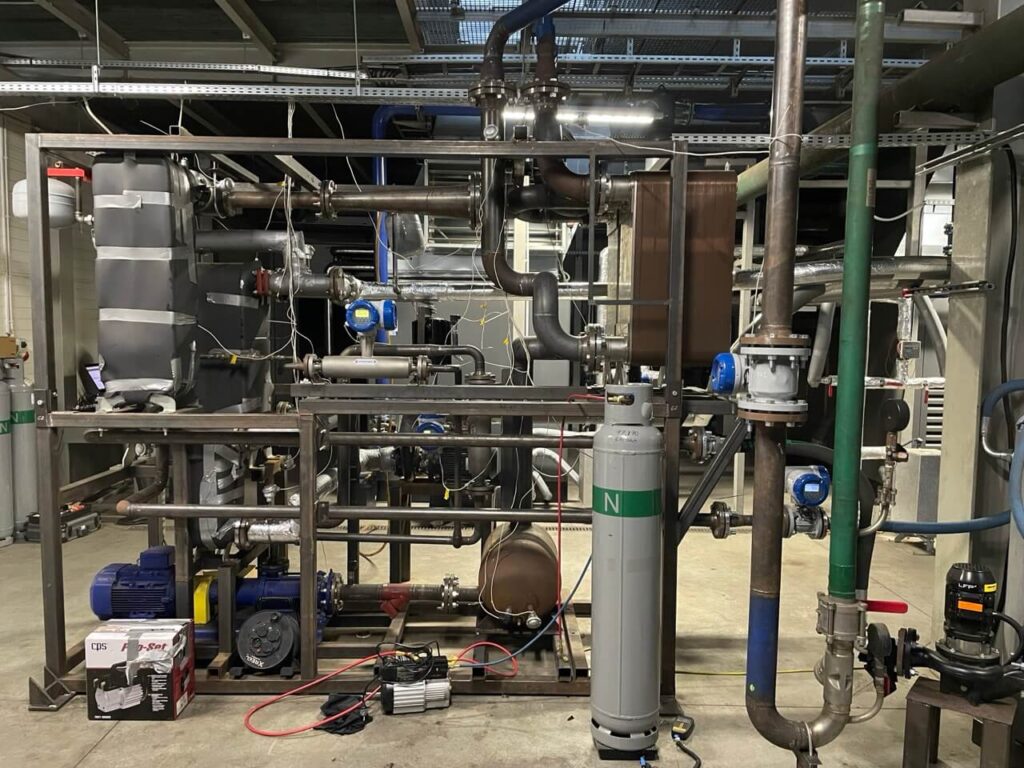
Home " Ejector-based refrigeration systems
Ejector-based refrigeration systems
MARANI JET-CHILLER - WASTE HEAT POWER GENERATION
Poland’s first technology for converting
waste heat into cooling capacity.
Original solution resulting from R&D work in collaboration with Bialystok University of Technology as part of a completed research project:
POIR.01.01.01-00-0301/18 entitled. "Development of two refrigeration systems, driven by 200 kW and 600 kW of waste heat capacity, adapted to chilled water temperature and high-temperature cooling".
Technology based on MARANI invention patent application “Ejector-based Refrigeration Unit”
Ejectors manufactured by the Research and Development Center of Pneumatic Components and Systems Ltd. in Kielce (MARANI Ltd. subsidiary)
Design of multi-ejector systems based on MARANI invention patent application “Tank collector”
Proprietary control system.

Supersonic ejector
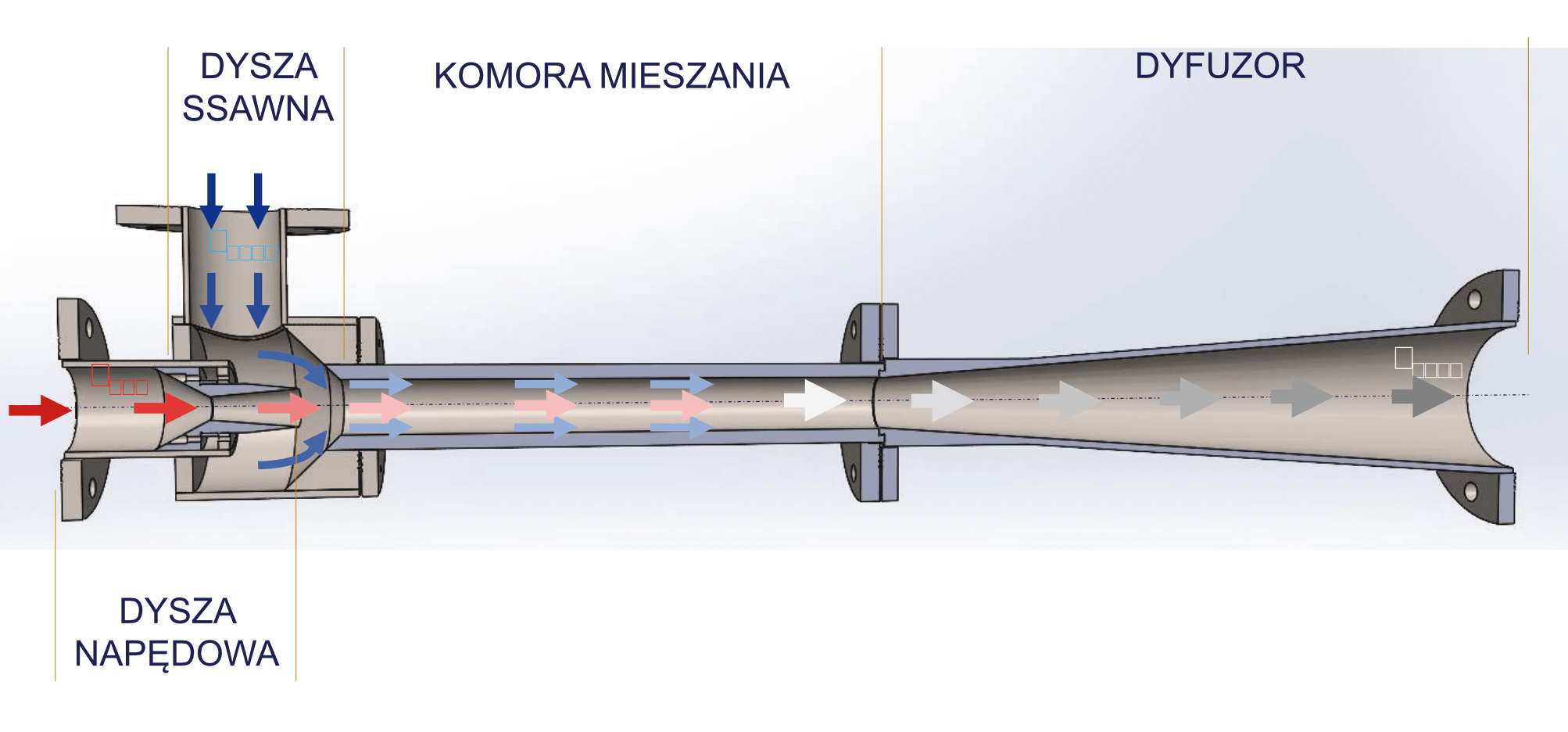
Characteristics of MARANI JET-CHILLER technology
- Pressure Equipment Directive (PED 2014/68/EU)
- Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC)
- Electromagnetic Compatibility Directives EMC (2014/30/EU)
- Low Voltage Directive LVD (2014/35/EU)
- Refrigeration standards EN 378-1+A1:2021-03 and EN 378-2:2017-03
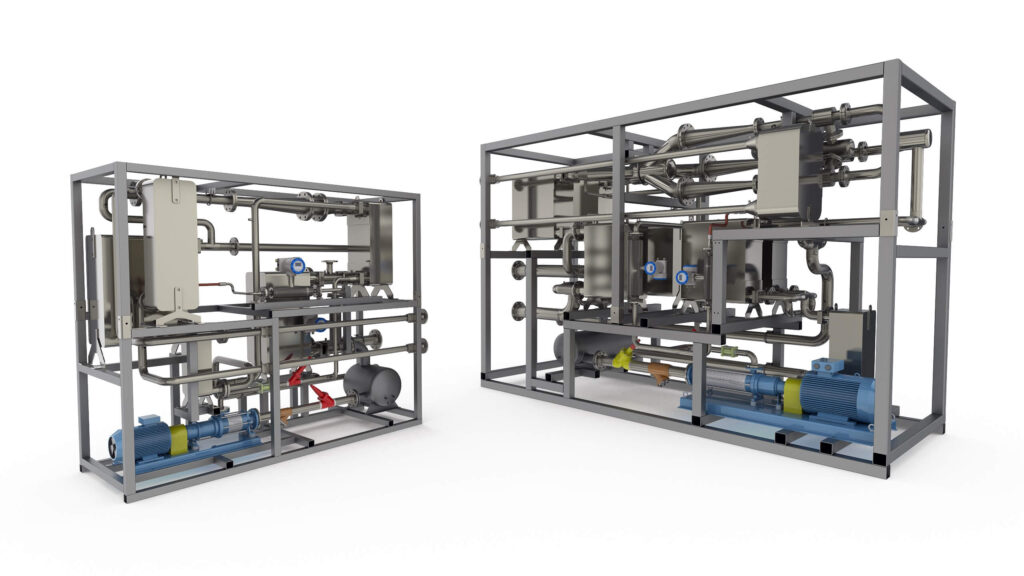
MARANI JET-CHILLER units
MARANI is a supplier of complete ejector-based refrigeration units designed, optimised and tailored to individual customer needs and conditions on the waste heat side. We offer chillers with driving thermal power from 100 to 600 kW. Depending on the conditions, a solution with a single chiller or several units working together is proposed, guaranteeing flexibility of operation depending on the available waste heat.
standard temperature cooling
MARANI JET-CHILLER STC
standard chilled water parameters 12oC/6oC COP from 0.25 for low temperature sources (~70oC) application for air-conditioning units
high temperature cooling
MARANI JET-CHILLER HTC
Benefits of development
waste heat for electricity generation
Energy efficiency assessment
The waste heat utilisation to generate cooling capacity influences the assessment of the energy efficiency of the entire plant, especially in the perspective of replacing existing standard cooling systems. The aspect of improving the energy efficiency of the entire industrial plant is particularly evident, when the cooling capacity is used to cool machinery, processes or process fluids, which has a direct impact on improving process parameters, further improving the efficiency of the final product manufacturing.
Economics
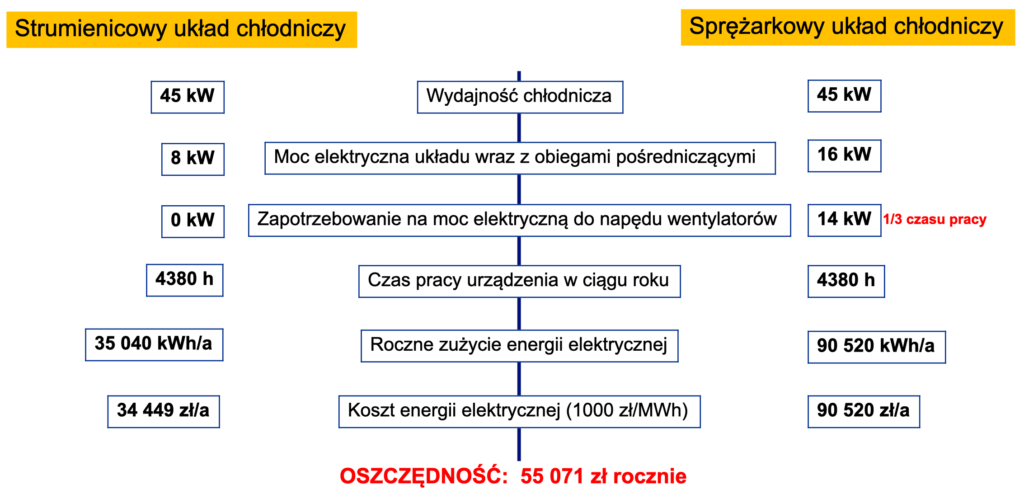
Generation of cooling capacity using Generation of cooling capacity using waste heat generates significant savings compared to a standard energy-intensive compressor cooling system, which is often used for chilled water cooling or for air conditioning purposes. If a source of waste heat is available, such systems can be confidently replaced by MARANI chillers. Below is an example calculation to compare the maintenance cost of the ejector-based refrigeration system with conventional compressor unit of the same cooling capacity.el, which also took into account the savings resulting from not having to switch on the cooler fans of the oil air compressors after waste heat collection was ensured.
Environment
The production of cooling capacity from waste heat, which was normally lost to the atmosphere through emissions and often requires the consumption of additional energy for its ejection, has a positive impact on the environment. Cooling capacity is produced with significantly less electricity consumption than in conventional refrigeration systems, without the additional carbon footprint created.
Competitive advantage
Technological process
The utilization of waste heat from the process, where it is necessary to lower the temperature of a medium, contributes to the optimisation of the process itself, by eliminating additional systems working only to lower the temperature. In such a case, there is an additional economic benefit by simultaneous implementation process cooling and additional low-temperature cooling capacity generation. It could be used in another process or for improving the comfort of employees.
Trigeneration
In the case of medium- and high-temperature heat sources, it is possible to compose a trigeneration system. Waste heat can be utilized in the first instance to drive the MARANI ORC system producing electricity. The cooled heat flow rate then be used to drive the MARANI CHILLER system generating cooling capacity. Subsequently, the heat from the lower sources of both systems (heat of condensation) can be used for heating purposes or the hot water production.
Image and value in business
Energy efficiency, waste heat recovery and self-generation of cooling capacity also have a positive impact on the assessment of the entrepreneur's attractiveness, maturity and technological and energy awareness. It adds value to the assessment of the enterprise by potential investors, investment financiers and decision-makers in business support programmes, or by the end customers themselves. The implementation of sustainable operations and the reduction of the carbon footprint contributes to brand value and market recognition.





